A wall-mounted sink is a fantastic choice for any bathroom, offering a minimalist aesthetic, easy cleaning, and the illusion of more space. However, their installation is not as straightforward as a pedestal or vanity sink. A professional installation relies on precision, proper support, and a keen eye for detail. This guide will walk you through the techniques and considerations that separate a DIY job from a flawless, long-lasting, and secure professional installation.
1. The Foundation: Planning and Preparation are Paramount
Before a single hole is drilled, a professional installer dedicates significant time to planning. This phase is critical for avoiding costly mistakes and ensuring a rock-solid result.
- Determine the Sink’s Weight and Dimensions: Wall-mounted sinks come in a variety of materials, from lightweight vitreous china to heavy concrete or solid surface. Knowing the sink’s exact weight is crucial for selecting the appropriate mounting hardware and determining if additional wall support is needed. Measure the sink’s width, depth, and height to plan for a comfortable and aesthetically pleasing position.
- Locate and Mark the Studs: The absolute first rule of a secure wall-mount installation is to anchor the sink to the wall studs, not just the drywall. Professionals use a high-quality stud finder to precisely locate the center of the studs behind the installation area. They then mark these locations with a pencil, as this is where the mounting hardware will be fastened.
- Establish the Correct Height: The standard height for a sink rim is 34 inches from the finished floor. However, this is just a guideline. Professionals will consider the user’s height and accessibility needs. The goal is to ensure the sink is comfortable for everyone who will use it. Use a level and a tape measure to mark the ideal height and center point on the wall.
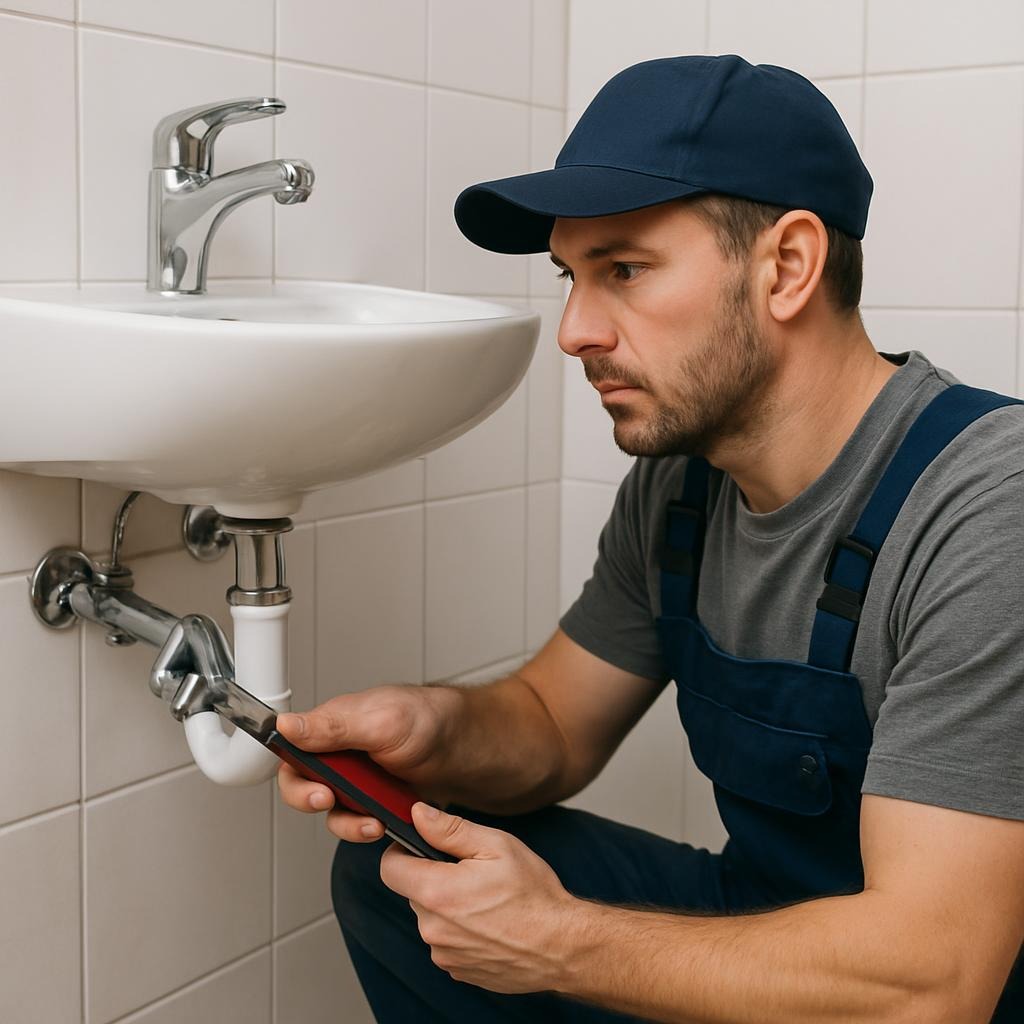
- Rough-In and Plumbing Considerations: If you are working in a new construction or during a major remodel, the plumbing rough-in must be perfectly aligned with the sink’s drain and faucet connections. An expert plumber will have already positioned the P-trap, supply lines, and drain pipe to match the sink’s specifications. For a retrofit installation, this might involve opening up the wall to relocate the plumbing.
2. The Anchoring: Choosing and Installing the Right Support System
This is arguably the most critical step. The long-term security of the sink depends entirely on the strength of its mounting system.
- The Wall-Mounted Bracket: Many wall-mounted sinks come with a manufacturer-supplied bracket. This bracket is designed to distribute the weight of the sink evenly. Professionals will use the provided template to precisely mark the bracket’s screw holes on the studs. Using a level, they will ensure the bracket is perfectly horizontal before driving the lag bolts or screws into the studs.
- Heavy-Duty Mounting Hardware: A professional never relies on the basic screws often included in a sink box. Instead, they use heavy-duty lag bolts or toggle bolts specifically rated for the sink’s weight. For particularly heavy sinks (over 100 lbs), some pros may opt for a special carrier system that bolts directly to the floor and studs, providing unmatched support.
- When Studs Aren’t an Option: If the studs are not conveniently located, a professional will not simply use drywall anchors. Instead, they will install horizontal blocking (usually a 2×6 or 2×8 piece of lumber) between two studs. This blocking provides a solid, continuous anchor point for the sink bracket, effectively creating a “new” stud where one is needed. This step often requires opening up the drywall, but it is the only way to guarantee a safe and secure installation.
3. The Installation: From Setting to Sealing
With the support system securely in place, the rest of the installation requires careful execution and attention to detail.
- Lifting and Positioning the Sink: This is often a two-person job, especially for heavier sinks. The sink must be carefully lifted and set onto the mounting bracket. Once in place, the professional will ensure it is perfectly level both horizontally and vertically. Minor adjustments may be needed at this point.
- Securing the Sink to the Bracket: Depending on the sink design, there may be set screws or fasteners that secure the sink to the bracket from below. These are tightened to prevent the sink from shifting or lifting off the bracket.
- Plumbing Connections: The professional will then connect the water supply lines and the P-trap to the drain assembly. They will use pipe wrenches and plumber’s tape or thread sealant on threaded connections to ensure a watertight seal. This is where experience is key—over-tightening can crack a connection, while under-tightening will lead to leaks.
- The Final Seal: Once all connections are made and the water is tested, a professional will apply a bead of high-quality silicone caulk along the top edge where the sink meets the wall. This is not for structural support but to prevent water from seeping behind the sink and into the wall, which could lead to mold or mildew. The caulk bead is applied cleanly and smoothly for a professional finish.
Final Thoughts: The Hallmarks of a Pro Installation
A professional wall-mounted sink installation isn’t just about putting a sink on the wall; it’s about engineering a secure, lasting solution. The hallmarks of a job well done are:
- No Movement: The finished sink feels absolutely solid and immovable.
- Perfectly Level: The sink is level in all directions.
- No Leaks: All plumbing connections are watertight.
- Clean Finish: The caulking is smooth and even, and the faucet and drain are installed without scratches or damage.
By understanding and following these professional techniques, you can ensure your wall-mounted sink installation is not only a stylish addition to your bathroom but a safe and durable one as well.

Leave a Reply